After decades of demolishing historic structures in the name of modernization and economic growth, China started to protected more and more cultural architecture relics. There are nearly 3,000 protected architecture cultural relics were named and listed on the National Cultural Relics Bureau.

From ancient to modern
As you can explore from the map, the data was showing all the architecture classifications from ancient eras to modern times, across over 4,000 years. Most of the ruins were in years of BC, mainly from Zhou Dynasty to South and North Dynasty. These eras also has the most tombs compare to other eras, for example, Qin Shi Huang Mausoleum tomb is a famous one in Qin Dynasty, and located in Xi’an, Shannxi province.
Note: The years showing is roughly the middles years of accordingly era. Using minus to showing the years that are before the Common Era.
The y-axis represents the percentage of classification in that era to the whole times.

The stream chart showing the proportion of cultural relics in different dynasties (registered), the different colors represent different cultural relic categories. The proportion of the number of cultural relics in different categories of different dynasties, the aesthetic and architectural changes in the era of the era.
Here are all the ancient architecture for first batch in the name list. Ming and Qing Dynasties have the most. The first batch is supposed to be the most important relics listed from Chinese government.
Hover over a circle to see the detail.
The Forbidden City is the former Chinese imperial palace from the Ming dynasty to the end of the Qing dynasty (the years 1420 to 1912). It served as the home of emperors and their households as well as the ceremonial and political center of Chinese government for almost 500 years.
Summer Palace another famous architecture. It is a vast ensemble of lakes, gardens and palaces in Beijing. It was an imperial garden in the Qing Dynasty.
Ming dynasty: from the Great Wall to the Forbidden City
The Ming dynasty constructed some of China’s most significant landmarks.
The span in which the Ming dynasty ruled China (1368–1644) was a period of incredible political and cultural growth for the nation. It was during this era that China commanded influence of much of East Asia, Vietnam, and Myanmar to the south, while also expanding its sphere of control to the Turks in the west. Yet, the reign of the Ming dynasty has come and gone. What remains, however, is the spectacular architecture produced during this time. Builders of the period made use of existing techniques but also incorporated brick into its great walls and palaces.
Here are some examples of the first batch of Ming Architecture on the protected relics list.
 Note: From left to right, top to bottom are: Beihai and Mission, Forbidden City, Great Wall Badaling, Great Wall Jiayuguan, Temple of Heaven, Zhenjue Temple King Kong Throne Wuta Temple tower, Great Wall Shanhaiguan, Potala Palace, Humble Administrator's Garden, Qidan Temple, Taer Temple, Xi'an City Wall.
Note: From left to right, top to bottom are: Beihai and Mission, Forbidden City, Great Wall Badaling, Great Wall Jiayuguan, Temple of Heaven, Zhenjue Temple King Kong Throne Wuta Temple tower, Great Wall Shanhaiguan, Potala Palace, Humble Administrator's Garden, Qidan Temple, Taer Temple, Xi'an City Wall. A sketch in region
Geologically, China could be divided into five areas: North China, South Central, Northwest, Southwest and East. If we see the map below in region, we could find that the architecture cultural relics are mainly in the intersect between North, Northwest and South Central.
The centralized relics in Shannxi, Henan and Shanxi also revealed the choices of dynasties's capital city. China has a vast territory since ancient times, and it is more difficult to manage. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the capital in a place with a middle position, which is conducive to the management of the country. In addition, the ancient traffic is backward, the waterway is the most convenient transportation route, and the strategic significance of Shaanxi and Henan is close to the Yellow River.
Feeling relics density
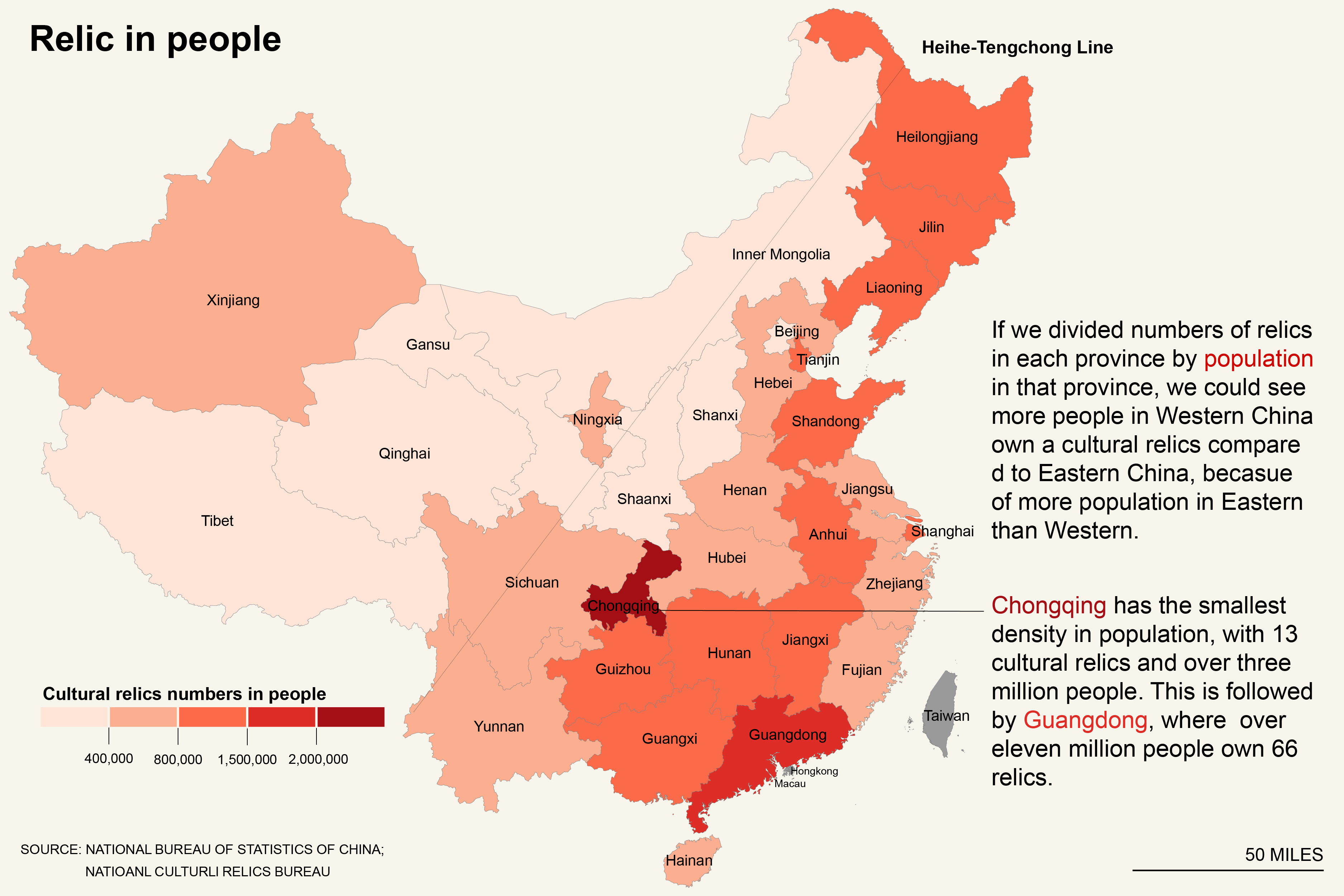
Here we measuring the density in two ways, firstly measure it in province population.
The Heihe-Tengchong line could also display the trend. According to statistics, west of the line has 57% of the area, but only 6% of the population; east of the line: 43% of the area, but 94% of the population. As you can see on the map.
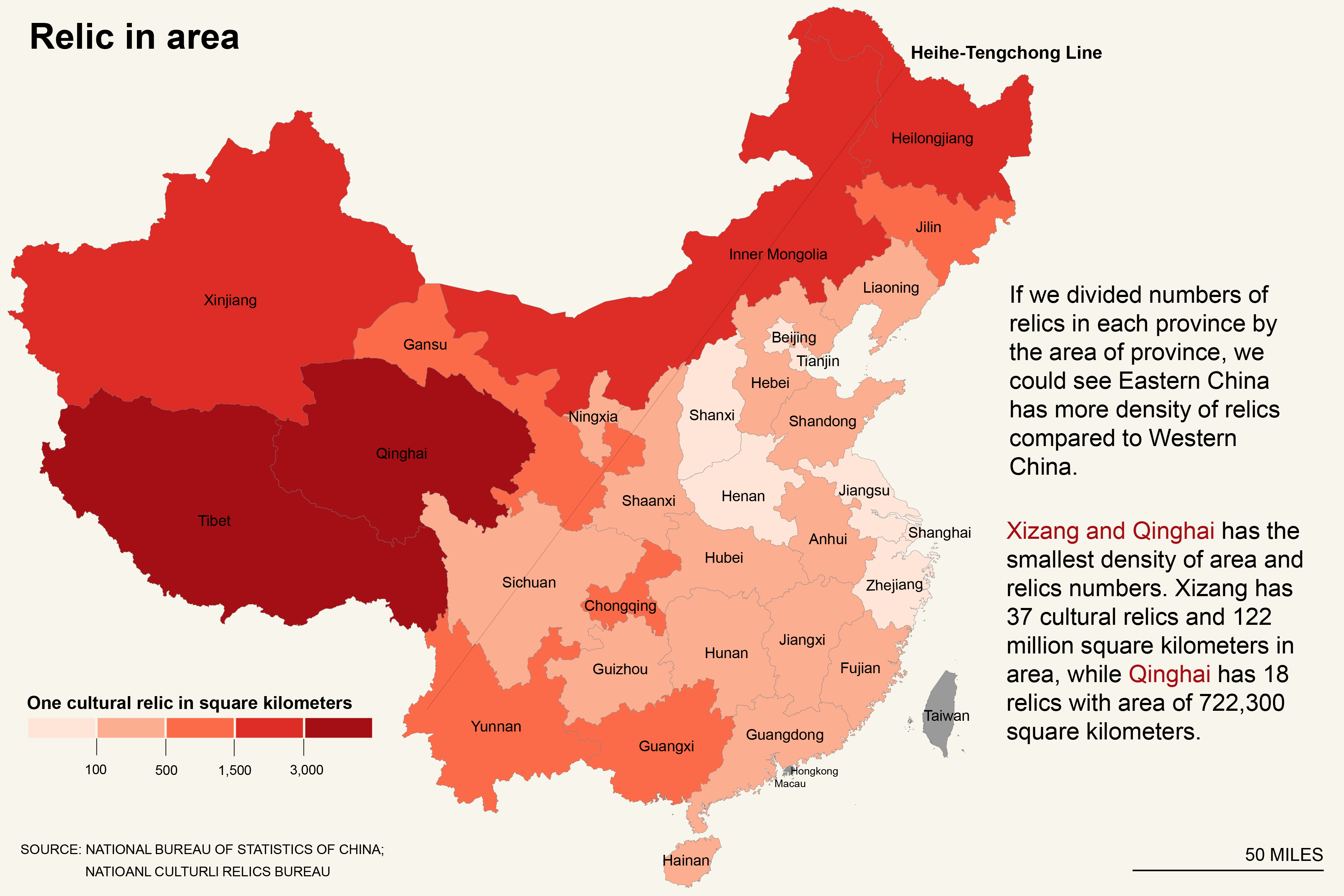
Then we measuring the density in province area. Accordingly, The Eastern part of China has smaller density.
Not only architecture relics, China will enhance cooperation in cultural relics protection with countries and regions participating in the Belt and Road Initiative, according to a guideline released by the general offices of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee and the State Council.
China will work with other countries in world cultural heritage application, archaeological studies, building cultural relic facilities and to put more high-quality cultural relics overseas for exhibitions to strengthen the influence of Chinese culture.